Learning objective: Estimate the expected shortfall given P/L or return data.
Questions:
708.1. A hedge fund's daily P/L for the last 300 trading days is plotted below in a histogram where the bin width is $0.20. Additionally, the worst 20 daily losses are sorted explicitly below the histogram:
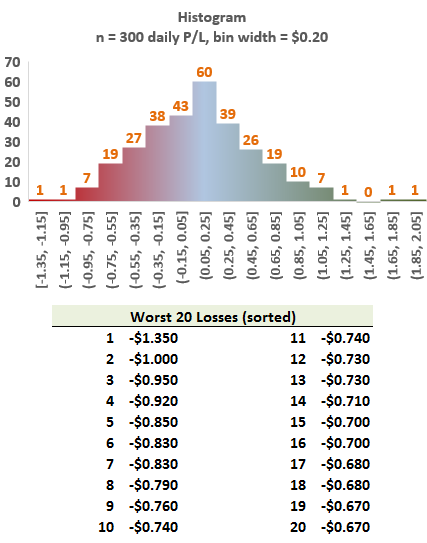
Which is nearest to the 99.0% expected shortfall (ES)?
a. 0.920
b. 0.950
c. 1.100
d. 1.350
708.2. The daily profit/loss (P/L) is given by the following discrete distribution where (a) is a constant:
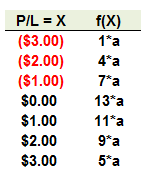
What is the 95.0% expected shortfall relative to zero (i.e., not relative to the mean or expected value)?
a. $1.50
b. $2.40
c. $2.67
d. $3.00
708.3. [This is more difficult than an exam-level question but gives practice to several concepts in Miller] At the end of an investment horizon, the final value of a risky investment will fall between zero and 10.0, inclusive, and is characterized by the probability density function f(x) = 3*x^2/1000, as plotted below.
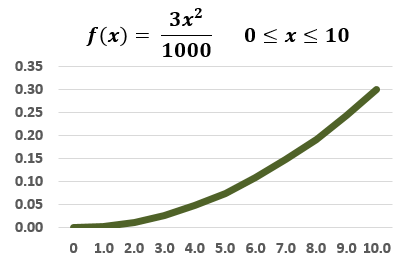
Let's define the 95.0% expected shortfall as the conditional loss relative to the expected future value of the asset; for example, if this asset's expected final value is +7.50, and if the 5.0% tail conditional expectation (TCE) is +1.0, then the 95.0% ES would be 6.50 as values to the left are losses and a final value of +1.0 would be a 6.50 loss relative to the expected value of 7.50.
Which is nearest to the 95.0% expected shortfall (ES)?
a. 2.76
b. 3.80
c. 4.74
d. 5.95
Answers here:
Questions:
708.1. A hedge fund's daily P/L for the last 300 trading days is plotted below in a histogram where the bin width is $0.20. Additionally, the worst 20 daily losses are sorted explicitly below the histogram:

Which is nearest to the 99.0% expected shortfall (ES)?
a. 0.920
b. 0.950
c. 1.100
d. 1.350
708.2. The daily profit/loss (P/L) is given by the following discrete distribution where (a) is a constant:

What is the 95.0% expected shortfall relative to zero (i.e., not relative to the mean or expected value)?
a. $1.50
b. $2.40
c. $2.67
d. $3.00
708.3. [This is more difficult than an exam-level question but gives practice to several concepts in Miller] At the end of an investment horizon, the final value of a risky investment will fall between zero and 10.0, inclusive, and is characterized by the probability density function f(x) = 3*x^2/1000, as plotted below.

Let's define the 95.0% expected shortfall as the conditional loss relative to the expected future value of the asset; for example, if this asset's expected final value is +7.50, and if the 5.0% tail conditional expectation (TCE) is +1.0, then the 95.0% ES would be 6.50 as values to the left are losses and a final value of +1.0 would be a 6.50 loss relative to the expected value of 7.50.
Which is nearest to the 95.0% expected shortfall (ES)?
a. 2.76
b. 3.80
c. 4.74
d. 5.95
Answers here:
Last edited by a moderator:
