Fran
Administrator
AIMs: Describe the short-term rate process under the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross (CIR) and Lognormal models. Calculate the short-term rate change and describe the basis point volatility using the CIR and Lognormal models. Summarize the application of a lognormal model with deterministic drift and a lognormal model with mean reversion
Questions:
307.1. Donald the analyst is employing the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross (CIR) model for the short-term rate process:
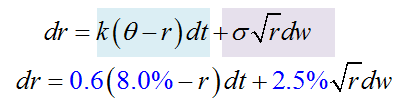
(Source: Bruce Tuckman, Fixed Income Securities, 3rd Edition (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2011))
His assumptions include (see above):
a. -0.250%
b. 0.444%
c. 1.390%
d. 2.172%
307.2. Peter the analyst is constructing a binomial tree according to Tuckman's lognormal model (without mean reversion). Here are his assumptions and partial tree (Source: Bruce Tuckman, Fixed Income Securities, 3rd Edition (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2011)):

His assumptions include:
a. 1.98665%
b. 2.05350%
c. 2.38794%
d. 3.12550%
307.3. Each of the following is true about lognormal models of the short-term interest rate process EXCEPT for:
a. In the lognormal models, the the natural logarithm of the short rate is normally distributed
b. Like the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross (CIR), the lognormal models offer the advantage of not allowing negative rates
c. The lognormal model without mean reversion is similar to the Ho-Lee model but based on the natural logarithm of the short rate instead of on the short rate itself
d. The Black-Karasinski Model is similar to the Ho-Lee Model but instead is an equilibrium model with constant drift
Answers:
Questions:
307.1. Donald the analyst is employing the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross (CIR) model for the short-term rate process:
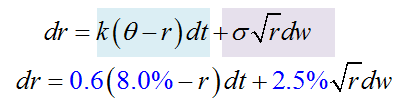
(Source: Bruce Tuckman, Fixed Income Securities, 3rd Edition (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2011))
His assumptions include (see above):
- The time-step is monthly, dt = 1/12
- Today's initial rate, r(0) = 1.00%
- The annual basis point volatility, sigma = 2.50%
- The long-run rate, theta = 8.00%
- The strength of reversion, k = 0.60
a. -0.250%
b. 0.444%
c. 1.390%
d. 2.172%
307.2. Peter the analyst is constructing a binomial tree according to Tuckman's lognormal model (without mean reversion). Here are his assumptions and partial tree (Source: Bruce Tuckman, Fixed Income Securities, 3rd Edition (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2011)):

His assumptions include:
- The time-step is monthly, dt = 1/12
- Today's initial rate, r(0) = 2.00%
- Annual drift is constant at 50 basis points
- The annual basis point volatility, sigma = 9.00%
a. 1.98665%
b. 2.05350%
c. 2.38794%
d. 3.12550%
307.3. Each of the following is true about lognormal models of the short-term interest rate process EXCEPT for:
a. In the lognormal models, the the natural logarithm of the short rate is normally distributed
b. Like the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross (CIR), the lognormal models offer the advantage of not allowing negative rates
c. The lognormal model without mean reversion is similar to the Ho-Lee model but based on the natural logarithm of the short rate instead of on the short rate itself
d. The Black-Karasinski Model is similar to the Ho-Lee Model but instead is an equilibrium model with constant drift
Answers:
