Learning Objectives: Compute the value of a European option using the Black-Scholes-Merton model on a dividend-paying stock, futures, and exchange rates. Describe warrants, calculate the value of a warrant, and calculate the dilution cost of the warrant to existing shareholders.
Questions:
24.18.1. As an analyst in a professional valuer firm, you have been asked to calculate the price of employee stock options assuming they are exercised only at the expiry. You have the following information:
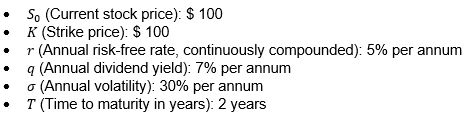
What is the correct value of a European call option?
a. $13.19
b. $16.74
c. $21.19
d. $11.68
24.18.2. A company with 1,000,000 existing shares is considering issuing 100,000 warrants, where each warrant gives the holder the right to buy one new share at a strike price of £50. The current market price of the stock is £55. Assuming markets are efficient and reflect the potential dilution from the outstanding warrants, what is closest to the cost of each warrant to existing shareholders?
a. £5.00
b. £4.50
c. £4.55
d. £5.50
24.18.3. A company currently has 2,000,000 shares outstanding and is considering issuing 200,000 warrants. Each warrant allows the holder to purchase one share at a strike price of USD 25. The current market price of the stock is USD 30. Assume the risk-free rate is 3% per annum, the volatility of the stock is 20% per annum, and the warrants have a maturity of 3 years. Calculate the value of one warrant using the Black-Scholes model modified for warrants and calculate the dilution cost of one warrant to existing shareholders.
a. Warrant Value: USD 8.25, Dilution Cost: USD 7.51
b. Warrant Value: USD 7.50, Dilution Cost: USD 8.25
c. Warrant Value: USD 8.00, Dilution Cost: USD 7.00
d. Warrant Value: USD 9.00, Dilution Cost: USD 8.00
Answers here:
Questions:
24.18.1. As an analyst in a professional valuer firm, you have been asked to calculate the price of employee stock options assuming they are exercised only at the expiry. You have the following information:
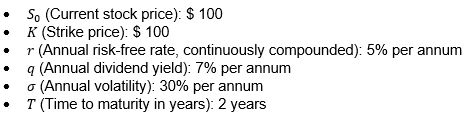
What is the correct value of a European call option?
a. $13.19
b. $16.74
c. $21.19
d. $11.68
24.18.2. A company with 1,000,000 existing shares is considering issuing 100,000 warrants, where each warrant gives the holder the right to buy one new share at a strike price of £50. The current market price of the stock is £55. Assuming markets are efficient and reflect the potential dilution from the outstanding warrants, what is closest to the cost of each warrant to existing shareholders?
a. £5.00
b. £4.50
c. £4.55
d. £5.50
24.18.3. A company currently has 2,000,000 shares outstanding and is considering issuing 200,000 warrants. Each warrant allows the holder to purchase one share at a strike price of USD 25. The current market price of the stock is USD 30. Assume the risk-free rate is 3% per annum, the volatility of the stock is 20% per annum, and the warrants have a maturity of 3 years. Calculate the value of one warrant using the Black-Scholes model modified for warrants and calculate the dilution cost of one warrant to existing shareholders.
a. Warrant Value: USD 8.25, Dilution Cost: USD 7.51
b. Warrant Value: USD 7.50, Dilution Cost: USD 8.25
c. Warrant Value: USD 8.00, Dilution Cost: USD 7.00
d. Warrant Value: USD 9.00, Dilution Cost: USD 8.00
Answers here:
