Learning objectives: Describe the factors that influence the level of market liquidity and the degree of liquidity resilience in markets. Identify drivers and their effects on market liquidity level and resilience. Assess the effects that monetary policy has on market liquidity. Explain how liquidity spillovers can be amplified and describe what effects this has on the market. Describe the recommendations to bolster the level of market liquidity and its resilience
703.1. In their Global Financial Stability Report, the IMF describes three broad categories of drivers of market liquidity levels and resilience (1) the risk appetite, funding constraints, and market risks faced by financial intermediaries, all of which affect their inclination to provide liquidity services and correct the mispricing of assets by taking advantage of arbitrage opportunities; (2) search costs, which influence the speed with which buyers and sellers can find each other; and (3) investor characteristics and behavior reflecting different mandates, constraints, and access to information. These drivers, in turn, are influenced by the following forces: macroeconomic environment, monetary policy, technology and regulation. These are illustrated by the IMF's diagram below except the arrows' colors have been disabled (also the diagram shows four drivers: Risk Appetite, Funding Market and Making, Search Costs, and Investor Base; as such, the three IMF categories reflect a bundling of the first two):
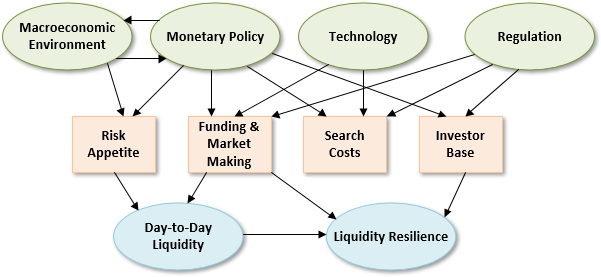
Each of the following statements accurately reflects the IMF's findings EXCEPT which is false?
a. Changes in the investor base have decreased liquidity risk and enabled higher liquidity resilience
b. Regulations had a mixed effects on market liquidity but reductions in market making harmed market liquidity
c. Although the impact of automated trades (algorithmic trading) is unclear, the net effect of technology has been to reduce search costs
d. Monetary policy has had an overall positive impact on market liquidity in recent years but may have increased liquidity risk; specifically, monetary policy had a positive effect on the "Risk Appetite" and "Funding & Market Making" drivers but likely a negative effect on "Search Costs" driver
703.2. Among the choices, which of the following is the BEST measure to identify liquidity spillover(s)?
a. Covariance between price change in time (t) and time (t-1)
b. Trade volume divided by market volume of outstanding securities
c. Co-movement across different asset classes and market economies
d. Slope coefficient of a regression of price change on signed order flow
703.3. Which of the following is true as a recommendation(s) by the IMF to bolster the level of market liquidity and its resilience?
a. During stress, central banks should expand the range of assets accepted as collateral for repo transactions
b. Promote greater ownership of corporate bonds by mutual funds because their daily redemption requirement increases market liquidity
c. Derivatives should be restricted; in particular, indirect short selling of sovereign debt via uncovered sovereign credit default swaps (SCDS) should be banned
d. Discourage further standardization in corporate bond markets because standardization increases volatility which, in turn, dampens liquidity
Answers here:
703.1. In their Global Financial Stability Report, the IMF describes three broad categories of drivers of market liquidity levels and resilience (1) the risk appetite, funding constraints, and market risks faced by financial intermediaries, all of which affect their inclination to provide liquidity services and correct the mispricing of assets by taking advantage of arbitrage opportunities; (2) search costs, which influence the speed with which buyers and sellers can find each other; and (3) investor characteristics and behavior reflecting different mandates, constraints, and access to information. These drivers, in turn, are influenced by the following forces: macroeconomic environment, monetary policy, technology and regulation. These are illustrated by the IMF's diagram below except the arrows' colors have been disabled (also the diagram shows four drivers: Risk Appetite, Funding Market and Making, Search Costs, and Investor Base; as such, the three IMF categories reflect a bundling of the first two):

Each of the following statements accurately reflects the IMF's findings EXCEPT which is false?
a. Changes in the investor base have decreased liquidity risk and enabled higher liquidity resilience
b. Regulations had a mixed effects on market liquidity but reductions in market making harmed market liquidity
c. Although the impact of automated trades (algorithmic trading) is unclear, the net effect of technology has been to reduce search costs
d. Monetary policy has had an overall positive impact on market liquidity in recent years but may have increased liquidity risk; specifically, monetary policy had a positive effect on the "Risk Appetite" and "Funding & Market Making" drivers but likely a negative effect on "Search Costs" driver
703.2. Among the choices, which of the following is the BEST measure to identify liquidity spillover(s)?
a. Covariance between price change in time (t) and time (t-1)
b. Trade volume divided by market volume of outstanding securities
c. Co-movement across different asset classes and market economies
d. Slope coefficient of a regression of price change on signed order flow
703.3. Which of the following is true as a recommendation(s) by the IMF to bolster the level of market liquidity and its resilience?
a. During stress, central banks should expand the range of assets accepted as collateral for repo transactions
b. Promote greater ownership of corporate bonds by mutual funds because their daily redemption requirement increases market liquidity
c. Derivatives should be restricted; in particular, indirect short selling of sovereign debt via uncovered sovereign credit default swaps (SCDS) should be banned
d. Discourage further standardization in corporate bond markets because standardization increases volatility which, in turn, dampens liquidity
Answers here:
Last edited by a moderator:
