Learning Objectives: Calculate the expected transactions cost and the spread risk factor for a transaction and calculate the liquidity adjustment to VaR for a position to be liquidated over a number of trading days. Discuss interactions between different types of liquidity risk and explain how liquidity risk events can increase systemic risk.
Questions:
24.3.1. Galaxy Investments, a hedge fund currently facing redemption pressures, is assessing the risk associated with a large position in a thinly traded stock. According to the fund's risk management policies, they need to evaluate the Value at Risk (VaR) for potentially liquidating this stock over a 10-day period to meet the redemption demands.
The original 99%-VaR, calculated without accounting for liquidity adjustments, currently stands at $5 million. What would be the most appropriate course of action to find the liquidity-adjusted VaR?
a. Increase the original VaR to $9.81 million to reflect potential liquidity constraints during the 10-day liquidation period.
b. Decrease the original VaR to $0.19 million, incorrectly assuming that extending the liquidation period reduces risk.
c. Make no changes to the VaR, incorrectly assuming it already accounts for liquidity risk.
d. Adjust the VaR to $15.81 million, inaccurately overestimating the necessary increase due to the 10-day liquidation period.
24.3.2. A risk analyst at Galaxy Trading is evaluating the transaction liquidity risk for their micro-cap stock portfolio. He has been tasked to provide a measure that uses the bid-ask spread as a key metric, observing that daily changes in the spread are normally distributed with a mean of zero and a constant variance.
Recent observation:
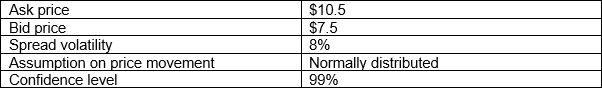
What would be the transaction cost risk at a 99% confidence interval, and what should be documented as the correct implication of this measure?
a. $9 +/- $4.6750; While useful, this method may not capture extreme scenarios where market conditions deviate significantly from the norm, potentially underestimating the risk during market turmoil.
b. $9 +/- $2.3375: While useful, this method may not capture extreme scenarios where market conditions deviate significantly from the norm, potentially underestimating the risk during market turmoil.
c. $9 +/- $2.3375; This method overestimates the liquidity risk by overly focusing on the spread behavior under normal distribution assumptions, ignoring the practical market scenarios where spreads can vary wildly.
d. $9 +/- $4.6750; This method overestimates the liquidity risk by overly focusing on the spread behavior under normal distribution assumptions, ignoring the practical market scenarios where spreads can vary wildly.
24.3.3. Centrebank Securities is involved in extensive tri-party repo transactions managed by major clearing banks. These systems, crucial for short-term financing, involve significant systemic risks due to their interconnected nature with the broader financial market infrastructure. Amid increasing market volatilities, there is a growing concern that any liquidity shortfall in these systems, particularly those facilitated by entities like the Bank of New York Mellon and JPMorgan Chase, could trigger wider financial disruptions.
Given Centrebank’s dependence on tri-party repo systems and the potential for widespread systemic impact due to liquidity constraints within these systems, which of the following strategies should be prioritized to effectively mitigate systemic risks?
a. Implement a more rigorous stress testing regime specifically for scenarios where tri-party repo systems face liquidity constraints, ensuring preparedness for potential disruptions.
b. Advocate for enhanced regulatory oversight and stress testing of major clearing banks to ensure they can withstand significant shocks without disrupting financial markets.
c. Develop a contingency plan that includes alternative financing mechanisms, reducing reliance on tri-party repos to prevent a cascade of failures in times of stress.
d. Increase transparency and real-time monitoring of liquidity positions both in-house and with all counterparties to quickly respond to emerging liquidity crises.
Answers here:
Questions:
24.3.1. Galaxy Investments, a hedge fund currently facing redemption pressures, is assessing the risk associated with a large position in a thinly traded stock. According to the fund's risk management policies, they need to evaluate the Value at Risk (VaR) for potentially liquidating this stock over a 10-day period to meet the redemption demands.
The original 99%-VaR, calculated without accounting for liquidity adjustments, currently stands at $5 million. What would be the most appropriate course of action to find the liquidity-adjusted VaR?
a. Increase the original VaR to $9.81 million to reflect potential liquidity constraints during the 10-day liquidation period.
b. Decrease the original VaR to $0.19 million, incorrectly assuming that extending the liquidation period reduces risk.
c. Make no changes to the VaR, incorrectly assuming it already accounts for liquidity risk.
d. Adjust the VaR to $15.81 million, inaccurately overestimating the necessary increase due to the 10-day liquidation period.
24.3.2. A risk analyst at Galaxy Trading is evaluating the transaction liquidity risk for their micro-cap stock portfolio. He has been tasked to provide a measure that uses the bid-ask spread as a key metric, observing that daily changes in the spread are normally distributed with a mean of zero and a constant variance.
Recent observation:

What would be the transaction cost risk at a 99% confidence interval, and what should be documented as the correct implication of this measure?
a. $9 +/- $4.6750; While useful, this method may not capture extreme scenarios where market conditions deviate significantly from the norm, potentially underestimating the risk during market turmoil.
b. $9 +/- $2.3375: While useful, this method may not capture extreme scenarios where market conditions deviate significantly from the norm, potentially underestimating the risk during market turmoil.
c. $9 +/- $2.3375; This method overestimates the liquidity risk by overly focusing on the spread behavior under normal distribution assumptions, ignoring the practical market scenarios where spreads can vary wildly.
d. $9 +/- $4.6750; This method overestimates the liquidity risk by overly focusing on the spread behavior under normal distribution assumptions, ignoring the practical market scenarios where spreads can vary wildly.
24.3.3. Centrebank Securities is involved in extensive tri-party repo transactions managed by major clearing banks. These systems, crucial for short-term financing, involve significant systemic risks due to their interconnected nature with the broader financial market infrastructure. Amid increasing market volatilities, there is a growing concern that any liquidity shortfall in these systems, particularly those facilitated by entities like the Bank of New York Mellon and JPMorgan Chase, could trigger wider financial disruptions.
Given Centrebank’s dependence on tri-party repo systems and the potential for widespread systemic impact due to liquidity constraints within these systems, which of the following strategies should be prioritized to effectively mitigate systemic risks?
a. Implement a more rigorous stress testing regime specifically for scenarios where tri-party repo systems face liquidity constraints, ensuring preparedness for potential disruptions.
b. Advocate for enhanced regulatory oversight and stress testing of major clearing banks to ensure they can withstand significant shocks without disrupting financial markets.
c. Develop a contingency plan that includes alternative financing mechanisms, reducing reliance on tri-party repos to prevent a cascade of failures in times of stress.
d. Increase transparency and real-time monitoring of liquidity positions both in-house and with all counterparties to quickly respond to emerging liquidity crises.
Answers here:
