Learning Objectives: Describe the relationship between leverage and a firm’s return profile (including the leverage effect) and distinguish the impact of different types of transactions on a firm’s leverage and balance sheet. Distinguish methods to measure and manage funding liquidity risk and transactions liquidity risk.
Questions:
24.2.1. Starwing Plc, a bank, has a current leverage ratio (TA/TE) of 2.45x ($27B/$11B). This is calculated based on the firm's assets of $27 billion and equity of $11 billion. The return on assets is consistently at 10%, while the cost of debt is 5%. The firm evaluates how different types of transactions might impact the firm's leverage and overall balance sheet. Given the above details on the bank's current financial structure and the volatile macro environment, which transaction should the bank undertake to manage leverage in order to minimize liquidity risk?
a. Raise $3 billion in equity.
b. Issue $3 billion debt.
c. Pay off $3 billion worth of debt by liquidating some of the assets.
d. Raise $1.5 billion in equity and $1.5 billion in debt.
24.2.2. Starling Homes, a real estate investment firm, is considering different financing options for buying residential properties on leverage. Starline is expecting a 20% annual increase in house prices. Starling is evaluating the impact of varying down payments and loan rates on its potential returns.
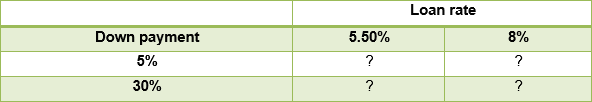
Given the expected price appreciation and the following financial conditions, which option should Starling Homes choose that would maximize returns?
a. Secure a loan with a 5% down payment, available at a 5.5% loan rate.
b. Secure a loan with a 30% down payment, available at an 8% loan rate.
c. Secure a loan with a 5% down payment, available at an 8% loan rate.
d. Secure a loan with a 30% down payment, available at a 5.5% loan rate.
24.2.3. Given Emerald Hedge Funds, susceptibility to sudden withdrawals by investors and counterparties, which of the following strategies would best help the fund manage its funding liquidity risks effectively?
a. Allocate a portion of the portfolio to high-quality, long-term bonds that offer a higher illiquidity premium, enhancing the fund’s ability to meet long-term liquidity needs.
b. Hold a higher proportion of assets in cash and highly liquid T-bills to readily meet sudden fund withdrawals.
c. Invest primarily in uncollateralized securities like highly rated agency bonds to enhance yield and generate higher returns to fund withdrawals.
d. Extend the duration of securities in the portfolio to lock in higher returns so more can be earned to meet the withdrawal demands.
Answers here:
Questions:
24.2.1. Starwing Plc, a bank, has a current leverage ratio (TA/TE) of 2.45x ($27B/$11B). This is calculated based on the firm's assets of $27 billion and equity of $11 billion. The return on assets is consistently at 10%, while the cost of debt is 5%. The firm evaluates how different types of transactions might impact the firm's leverage and overall balance sheet. Given the above details on the bank's current financial structure and the volatile macro environment, which transaction should the bank undertake to manage leverage in order to minimize liquidity risk?
a. Raise $3 billion in equity.
b. Issue $3 billion debt.
c. Pay off $3 billion worth of debt by liquidating some of the assets.
d. Raise $1.5 billion in equity and $1.5 billion in debt.
24.2.2. Starling Homes, a real estate investment firm, is considering different financing options for buying residential properties on leverage. Starline is expecting a 20% annual increase in house prices. Starling is evaluating the impact of varying down payments and loan rates on its potential returns.

Given the expected price appreciation and the following financial conditions, which option should Starling Homes choose that would maximize returns?
a. Secure a loan with a 5% down payment, available at a 5.5% loan rate.
b. Secure a loan with a 30% down payment, available at an 8% loan rate.
c. Secure a loan with a 5% down payment, available at an 8% loan rate.
d. Secure a loan with a 30% down payment, available at a 5.5% loan rate.
24.2.3. Given Emerald Hedge Funds, susceptibility to sudden withdrawals by investors and counterparties, which of the following strategies would best help the fund manage its funding liquidity risks effectively?
a. Allocate a portion of the portfolio to high-quality, long-term bonds that offer a higher illiquidity premium, enhancing the fund’s ability to meet long-term liquidity needs.
b. Hold a higher proportion of assets in cash and highly liquid T-bills to readily meet sudden fund withdrawals.
c. Invest primarily in uncollateralized securities like highly rated agency bonds to enhance yield and generate higher returns to fund withdrawals.
d. Extend the duration of securities in the portfolio to lock in higher returns so more can be earned to meet the withdrawal demands.
Answers here:
