Learning Objectives: Estimate operational risk exposures based on the fault tree model given probability assumptions. Describe approaches used to determine the level of operational risk capital for economic capital purposes, including their application and limitations. Describe and explain the steps to ensure a strong level of operational resilience and to test the operational resilience of important business services.
Questions:
24.4.1. FX Trade, a proprietary trading firm, is evaluating the adequacy of its capital amidst recent governance issues. A risk manager has used a fault tree model to estimate the expected loss from a rogue trader. The model identifies five conditions necessary for a loss to occur, with their respective probabilities:
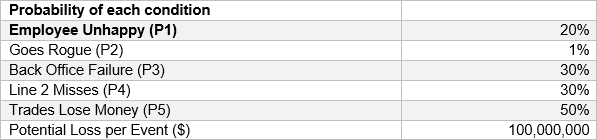
Assuming all conditions are independent, the probability of all conditions occurring simultaneously, leading to a financial loss, has been calculated.
If a firm has 1,000 traders, and each rogue trade under these conditions is assumed to result in a loss of $100,000,000, what is the total exposure for the firm?
a. $9000
b. $9,000,000
c. $30,000
d. $50,000,000
24.4.2. In the aftermath of a cyber-attack that cost FX Banco $500 million in losses, the bank is developing a model to calculate operational risk capital for economic capital purposes. The bank has comprehensive internal data on frequent operational losses, such as minor process failures, but it is also concerned with accurately modeling rare, extreme events like major fraud or cyber-attacks. The bank wants to use a method that allows it to address infrequent but large, catastrophic losses in a balanced way.
Which of the following approaches should FX Banco choose?
a. A method that estimates operational risk capital based on a percentage of the bank's gross income. While easy to implement, it does not account for specific loss events or their severity.
b. A method that separately models the frequency and severity of losses and combines them using statistical simulations. This approach is effective for regular losses but may not be as precise for extreme, catastrophic events.
c. A method that focuses on extreme events by using statistical techniques to model the tail of the loss distribution. This method is highly effective at estimating the impact of rare, large losses but may not adequately capture frequent, smaller losses.
d. A method that combines a general loss modeling approach with additional techniques specifically designed to improve the accuracy of extreme event estimation, effectively balancing both frequent, smaller losses and rare, catastrophic losses.
24.4.3. Zlich Finance, a fast-growing UK-based FinTech consumer lending firm, offers various services such as digital wallets, savings accounts, investment portfolios, debit cards, lending and borrowing, and FX remittances that allow customers to make payments in different currencies and meet their day-to-day consumer needs. A senior operations manager at the firm is developing a plan to comply with new UK regulatory requirements for operational resilience.
Which of the following steps should the manager recommend for the firm to best comply with regulatory expectations in this area?
a. Develop an impact tolerance for each of the important business services provided by the firm.
b. Self-assessment by the board every 5 years to ensure longer-term coverage.
c. Use 1-year 99.9% VaR to Calculate the operational risk for each of the firm’s business divisions and use this result to reserve additional capital for each division.
d. Immediately establish lines of communication after a breach incident has occurred.
Answers here:
Questions:
24.4.1. FX Trade, a proprietary trading firm, is evaluating the adequacy of its capital amidst recent governance issues. A risk manager has used a fault tree model to estimate the expected loss from a rogue trader. The model identifies five conditions necessary for a loss to occur, with their respective probabilities:

Assuming all conditions are independent, the probability of all conditions occurring simultaneously, leading to a financial loss, has been calculated.
If a firm has 1,000 traders, and each rogue trade under these conditions is assumed to result in a loss of $100,000,000, what is the total exposure for the firm?
a. $9000
b. $9,000,000
c. $30,000
d. $50,000,000
24.4.2. In the aftermath of a cyber-attack that cost FX Banco $500 million in losses, the bank is developing a model to calculate operational risk capital for economic capital purposes. The bank has comprehensive internal data on frequent operational losses, such as minor process failures, but it is also concerned with accurately modeling rare, extreme events like major fraud or cyber-attacks. The bank wants to use a method that allows it to address infrequent but large, catastrophic losses in a balanced way.
Which of the following approaches should FX Banco choose?
a. A method that estimates operational risk capital based on a percentage of the bank's gross income. While easy to implement, it does not account for specific loss events or their severity.
b. A method that separately models the frequency and severity of losses and combines them using statistical simulations. This approach is effective for regular losses but may not be as precise for extreme, catastrophic events.
c. A method that focuses on extreme events by using statistical techniques to model the tail of the loss distribution. This method is highly effective at estimating the impact of rare, large losses but may not adequately capture frequent, smaller losses.
d. A method that combines a general loss modeling approach with additional techniques specifically designed to improve the accuracy of extreme event estimation, effectively balancing both frequent, smaller losses and rare, catastrophic losses.
24.4.3. Zlich Finance, a fast-growing UK-based FinTech consumer lending firm, offers various services such as digital wallets, savings accounts, investment portfolios, debit cards, lending and borrowing, and FX remittances that allow customers to make payments in different currencies and meet their day-to-day consumer needs. A senior operations manager at the firm is developing a plan to comply with new UK regulatory requirements for operational resilience.
Which of the following steps should the manager recommend for the firm to best comply with regulatory expectations in this area?
a. Develop an impact tolerance for each of the important business services provided by the firm.
b. Self-assessment by the board every 5 years to ensure longer-term coverage.
c. Use 1-year 99.9% VaR to Calculate the operational risk for each of the firm’s business divisions and use this result to reserve additional capital for each division.
d. Immediately establish lines of communication after a breach incident has occurred.
Answers here:
