Learning objectives: Describe challenges faced by banks with respect to conduct and culture and explain motivations for banks to improve their conduct and culture. Explain methods by which a bank can improve its corporate culture and assess progress made by banks in this area. Explain how a bank can structure performance incentives and make staff development decisions to encourage a strong corporate culture. Summarize expectations by different national regulators for banks’ conduct and culture. Describe best practices and lessons learned in managing a bank’s corporate culture.
Questions:
20.1.1. Culture is famously difficult to define. The Financial Risk Manager (FRM) says that risk culture “can be thought of as the set of goals, values, beliefs, procedures, customs, and conventions that influence how staff create, identify, manage, and think about risk within an enterprise, including implicit and explicit beliefs." By comparison, the G30's simplified framework (see image below) asserts that bank culture is one of the key inputs that determines the bank's outcomes.
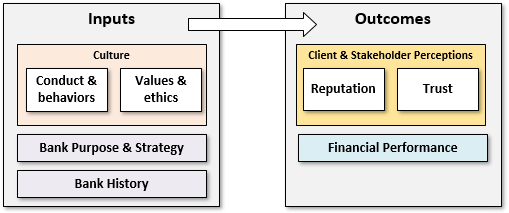
Specifically, the G30 defines culture as "the mechanism that delivers the values and behaviors that shape conduct and contributes to creating trust in banks and a positive reputation for banks among key stakeholders, both internal and external." Which of the following statements about culture is TRUE?
a. Cultural norms and beliefs can be easily measured
b. Conduct can be measured and should be measured
c. Cultural outcomes by definition are not objective
d. In general, cultures are empirically either right (aka, good) or wrong (aka, bad)
20.1.2. After years of progress on improving banking culture and conduct, industry leaders have reported eight important lessons they learned during the process. Among these lessons learned, which of the following is TRUE?
a. Diversity is orthogonal to (independent of) cultural outcomes
b. Regulation has a key and important role to play in cultural outcomes
c. The ideal mechanism for managing culture is an annual off-site event
d. Conduct includes unintended consequences of decisions and/or lack of knowledge
20.1.3. The G30 examined other industries (that is, aside from the banking industry) in order to identify the common characteristics that tend to lead to cultural breakdowns. With respect to the cross-industry lessons learned, each of the following is true as an industry characteristic that can lead to greater culture risk EXCEPT which does NOT lead to greater culture risk?
a. Misaligned incentives
b. Presence of dominant companies
c. High utilization of technology
d. High dependence on specialized skills
Answers here:
Questions:
20.1.1. Culture is famously difficult to define. The Financial Risk Manager (FRM) says that risk culture “can be thought of as the set of goals, values, beliefs, procedures, customs, and conventions that influence how staff create, identify, manage, and think about risk within an enterprise, including implicit and explicit beliefs." By comparison, the G30's simplified framework (see image below) asserts that bank culture is one of the key inputs that determines the bank's outcomes.

Specifically, the G30 defines culture as "the mechanism that delivers the values and behaviors that shape conduct and contributes to creating trust in banks and a positive reputation for banks among key stakeholders, both internal and external." Which of the following statements about culture is TRUE?
a. Cultural norms and beliefs can be easily measured
b. Conduct can be measured and should be measured
c. Cultural outcomes by definition are not objective
d. In general, cultures are empirically either right (aka, good) or wrong (aka, bad)
20.1.2. After years of progress on improving banking culture and conduct, industry leaders have reported eight important lessons they learned during the process. Among these lessons learned, which of the following is TRUE?
a. Diversity is orthogonal to (independent of) cultural outcomes
b. Regulation has a key and important role to play in cultural outcomes
c. The ideal mechanism for managing culture is an annual off-site event
d. Conduct includes unintended consequences of decisions and/or lack of knowledge
20.1.3. The G30 examined other industries (that is, aside from the banking industry) in order to identify the common characteristics that tend to lead to cultural breakdowns. With respect to the cross-industry lessons learned, each of the following is true as an industry characteristic that can lead to greater culture risk EXCEPT which does NOT lead to greater culture risk?
a. Misaligned incentives
b. Presence of dominant companies
c. High utilization of technology
d. High dependence on specialized skills
Answers here:
