Learning Objectives: Explain the capital adequacy, asset quality, management, earnings, and liquidity (CAMEL) system used for evaluating the financial condition of a bank. Describe quantitative measurements and factors of credit risk, including probability of default, loss given default, exposure at default, expected loss, and time horizon. Estimate capital adequacy ratio of a financial institution. Describe the judgmental approaches, empirical models, and financial models to predict default.
Questions:
24.6.1. Maple Consultants made the following observations on Marble Bank using the CAMEL system:
a. Capital adequacy is strong; management changes are recent but promising.
b. Asset quality is becoming a concern due to rising delinquencies in mortgages; earnings have been consistently strong.
c. Liquidity positions are below regulatory requirements, and asset quality shows signs of deterioration.
d. Management has been effective in strategy implementation; liquidity coverage ratios meet the required standards.
24.6.2. When writing a credit risk assessment report for the risk committee, a junior credit risk analyst includes several statements about the core components and their implications. The credit risk manager reviews the report and highlights the following statements.
a. 1 and 2
b. 1, 3 and 4
c. 2, 4 and 5
d. All of them
24.6.3. After a thorough audit, concerns were raised about the credit risk assessment methodologies applied by the credit risk department on the borrowers of Mancus Lending Group Limited. Mancus, a UK-based financial institution, is a key player in the real estate lending market, serving a broad range of borrowers, from individual homeowners to major real estate developers. To address these concerns, a special board meeting was called to explore and select a new credit risk model. Notably, three board members proposed different alternatives based on their potential benefits for Mancus’s complex lending environment.
a. Moe's judgmental approach
b. Larry's CreditMetrics™ approach.
c. Curly's Merton Model approach.
d. All of them.
24.6.4. Assess Company XYZ's capital adequacy over the last three years, as measured by the three key capital ratios.
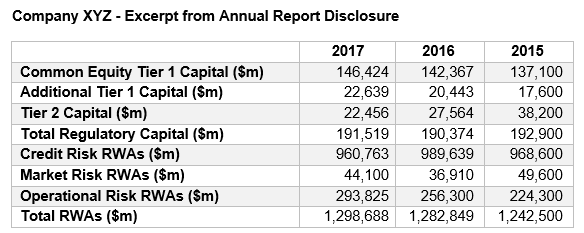
Based on the above, Company XYZ’s capital adequacy over the last three years, as measured by the three key capital ratios, signals which of the following conditions?
a. Mixed
b. Declining
c. Improving
d. Not enough data to determine
Answers here:
Questions:
24.6.1. Maple Consultants made the following observations on Marble Bank using the CAMEL system:
- Marble Bank maintains a capital-to-risk-weighted assets ratio (CRAR) of 15%, well above the regulatory minimum of 10%, indicating strong capital adequacy to support risks.
- A significant portion of Marble Bank’s loan portfolio is in long-term, fixed-rate mortgages, which have started to show an increase in delinquencies over the past year.
- The bank's management team has recently been restructured, with several new appointments from within the banking sector, though their effectiveness in implementing strategy remains to be seen.
- Despite a challenging economic environment, Marble Bank has reported a consistent increase in net income over the past three years, demonstrating robust earnings capacity.
- Marble Bank's liquidity coverage ratio (LCR) is below the required 100%, indicating potential challenges in meeting short-term obligations without additional funding.
a. Capital adequacy is strong; management changes are recent but promising.
b. Asset quality is becoming a concern due to rising delinquencies in mortgages; earnings have been consistently strong.
c. Liquidity positions are below regulatory requirements, and asset quality shows signs of deterioration.
d. Management has been effective in strategy implementation; liquidity coverage ratios meet the required standards.
24.6.2. When writing a credit risk assessment report for the risk committee, a junior credit risk analyst includes several statements about the core components and their implications. The credit risk manager reviews the report and highlights the following statements.
- "The Probability of Default (PD) for a loan is identical to its hazard rate, directly indicating the instant rate at which borrowers are expected to default per year, regardless of the loan's term or the time already elapsed without default."
- "LGD measures the total amount of credit extended to a borrower that is likely to be recovered immediately after a default event, indicating a direct recovery rate without considering the collateral's value or sale costs."
- "EAD is the minimum amount that a lender is guaranteed to recover when a borrower defaults, fixed at the initiation of the loan and unaffected by changes in credit line usage or market conditions."
- "Expected Loss is calculated solely based on the historical default rate of similar loans, serving as a static measure that remains unchanged throughout the life of a loan."
- "The time horizon for assessing credit risk is typically set to a standard one-year period for all types of loans and credit facilities, regardless of the loan term or the borrower's specific risk profile."
a. 1 and 2
b. 1, 3 and 4
c. 2, 4 and 5
d. All of them
24.6.3. After a thorough audit, concerns were raised about the credit risk assessment methodologies applied by the credit risk department on the borrowers of Mancus Lending Group Limited. Mancus, a UK-based financial institution, is a key player in the real estate lending market, serving a broad range of borrowers, from individual homeowners to major real estate developers. To address these concerns, a special board meeting was called to explore and select a new credit risk model. Notably, three board members proposed different alternatives based on their potential benefits for Mancus’s complex lending environment.
- Moe: "We can't overlook the human element. Our judgment is nuanced, capable of catching what models might miss, especially in the real estate sector."
- Larry: "Historical data is key. With CreditMetrics™, we have a systematic way to estimate defaults, applying a robust Value-at-Risk framework that’s proven effective."
- Curly: "But consider the Merton Model's precision. It uses market data to assess the risk, bringing a level of financial insight that traditional methods can’t."
a. Moe's judgmental approach
b. Larry's CreditMetrics™ approach.
c. Curly's Merton Model approach.
d. All of them.
24.6.4. Assess Company XYZ's capital adequacy over the last three years, as measured by the three key capital ratios.

Based on the above, Company XYZ’s capital adequacy over the last three years, as measured by the three key capital ratios, signals which of the following conditions?
a. Mixed
b. Declining
c. Improving
d. Not enough data to determine
Answers here:

