Learning Objectives: Describe a credit derivative, credit default swap (CDS), total return swap, and collateralized debt obligation (CDO). Explain how to account for credit risk exposure in valuing a CDS. Identify the default probabilities used to value a CDS. Evaluate the use of credit indices and fixed coupons in pricing CDS transactions.
Questions:
24.22.1. Sesame Street Bank has engaged in several complex credit derivative transactions as part of its risk management and investment strategy. The bank's portfolio includes:
Given the potential increase in defaults and rising interest rate environment, which strategy should Sesame Street Investment Bank prioritize to manage its exposure effectively?
a. Extend CDS Coverage: Purchase additional CDS protection to include residential mortgages within the CDO, anticipating higher default rates in this segment due to rising interest rates.
b. Revise TRS Terms: Renegotiate the TRS to receive a variable rate instead of a fixed rate, reducing potential losses if SOFR rises as predicted.
c. Diversify the Equity Tranche: Sell a portion of the equity tranche to other institutional investors to reduce concentration risk and enhance liquidity, using the proceeds to bolster other defensive financial instruments.
d. Consolidate Holdings: Focus on buying out mezzanine and senior tranches of other CDOs to stabilize returns and reduce overall portfolio volatility.
24.22.2. In November 2021, you are tasked with evaluating a 5-year CDS entered on March 20, 2020, involving a notional principal of $100 million. The CDS was purchased to hedge against the default of a particular corporate reference entity. The buyer agreed to pay an annual rate of 90 basis points, with payments made quarterly in arrears.
Market conditions shifted, and there's speculation about the reference entity's creditworthiness. Recent auction data suggests fluctuations in bond prices, and there is a potential risk of default within the next financial quarter. The current mid-market value of the cheapest deliverable bond from the reference entity is $35 per $100 of face value. The auction data corresponds to an ISDA-organized auction following a credit event.
Below are the cumulative default probabilities and survival probabilities over the next five years, estimated at the beginning of the CDS contract:
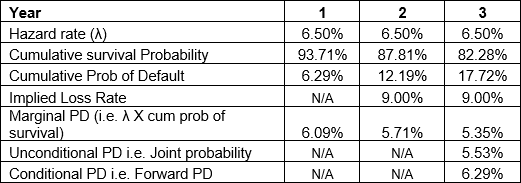
Calculate the expected payoff and its present value for the third year of the CDS contract.
a. $3.532M
b. $14.844M.
c. $3.479M.
d. $3.402M
24.22.3. Alex is evaluating a potential 5-year CDS index trade using the iTraxx Europe Index, currently quoted at 45bps with a fixed coupon of 50bps. The recovery rate is 35%. Alex's calculations suggest an implied hazard rate of 0.681% and a contract duration of 4.6 years. The yield curve is flat at 3.5% per year, continuously compounded.
Which analysis should Alex prioritize to assess the financial soundness of this trade?
a. Confirm the accuracy of the pricing formula and payments.
b. Evaluate the impact of flat 3.5% yield curve t.
c. Conduct sensitivity analysis on 35% recovery rate.
d. Analyze implications of hazard rate and defaults on contract value.
Answers here:
Questions:
24.22.1. Sesame Street Bank has engaged in several complex credit derivative transactions as part of its risk management and investment strategy. The bank's portfolio includes:
- Collateralized Debt Obligation (CDO) that pools high-yield corporate loans and residential mortgages. Sesame Street is holding a significant portion of the riskier equity tranche.
- Credit Default Swaps (CDS) protection from Solvency Insurance Corp. focuses on the CDO's corporate loan components.
- Total Return Swaps (TRS), where it exchanges the total economic performance of a $200 million bond portfolio for a fixed payment plus a margin based on SOFR with a hedge fund. This is intended to hedge interest rate risk, allowing Sesame Street to capitalize on bond market gains.
Given the potential increase in defaults and rising interest rate environment, which strategy should Sesame Street Investment Bank prioritize to manage its exposure effectively?
a. Extend CDS Coverage: Purchase additional CDS protection to include residential mortgages within the CDO, anticipating higher default rates in this segment due to rising interest rates.
b. Revise TRS Terms: Renegotiate the TRS to receive a variable rate instead of a fixed rate, reducing potential losses if SOFR rises as predicted.
c. Diversify the Equity Tranche: Sell a portion of the equity tranche to other institutional investors to reduce concentration risk and enhance liquidity, using the proceeds to bolster other defensive financial instruments.
d. Consolidate Holdings: Focus on buying out mezzanine and senior tranches of other CDOs to stabilize returns and reduce overall portfolio volatility.
24.22.2. In November 2021, you are tasked with evaluating a 5-year CDS entered on March 20, 2020, involving a notional principal of $100 million. The CDS was purchased to hedge against the default of a particular corporate reference entity. The buyer agreed to pay an annual rate of 90 basis points, with payments made quarterly in arrears.
Market conditions shifted, and there's speculation about the reference entity's creditworthiness. Recent auction data suggests fluctuations in bond prices, and there is a potential risk of default within the next financial quarter. The current mid-market value of the cheapest deliverable bond from the reference entity is $35 per $100 of face value. The auction data corresponds to an ISDA-organized auction following a credit event.
Below are the cumulative default probabilities and survival probabilities over the next five years, estimated at the beginning of the CDS contract:

Calculate the expected payoff and its present value for the third year of the CDS contract.
a. $3.532M
b. $14.844M.
c. $3.479M.
d. $3.402M
24.22.3. Alex is evaluating a potential 5-year CDS index trade using the iTraxx Europe Index, currently quoted at 45bps with a fixed coupon of 50bps. The recovery rate is 35%. Alex's calculations suggest an implied hazard rate of 0.681% and a contract duration of 4.6 years. The yield curve is flat at 3.5% per year, continuously compounded.
Which analysis should Alex prioritize to assess the financial soundness of this trade?
a. Confirm the accuracy of the pricing formula and payments.
b. Evaluate the impact of flat 3.5% yield curve t.
c. Conduct sensitivity analysis on 35% recovery rate.
d. Analyze implications of hazard rate and defaults on contract value.
Answers here:
