Learning objectives: Calculate the value of an American and a European call or put option using a one-step and two-step binomial model. Describe how volatility is captured in the binomial model.
Questions:
811.1 Consider a six-month at-the-money (ATM) European call option on a non-dividend-paying stock with a current price of $80.00. Peter the Risk Analyst has employed a two-step (i.e., three months per step) binomial model to price the option, as displayed below:
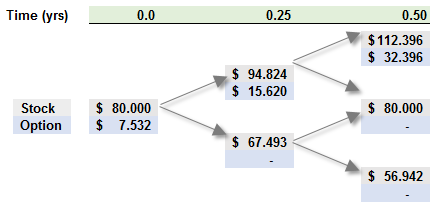
Peter's model matches the up and down movements to his estimate of the stock's prospective volatility, which he assumes is 34.0% per annum. The risk-free rate is 4.0%. Which of the following is nearest to the risk-neutral probability of the stock price going up in a single step?
a. 45.61%
b. 46.44%
c. 48.70%
d. 52.52%
811.2. Consider a European call option on a non-dividend-paying stock. The strike price is $80.00 while the stock price is currently $90.00. Barbara the Risk Analyst employs a two-step (i.e., three months per step) binomial model to price the option, as shown below:
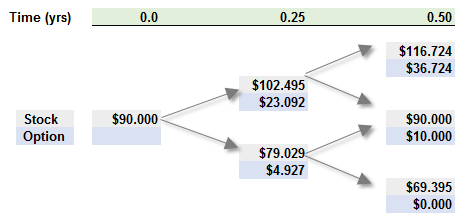
Barbara estimates the volatility of the stock is 26.0%, and she assumes the riskfree rate is 3.0%. Which of the following is nearest to her estimate of the price of the option?
a. $12.97
b. $13.84
c. $14.35
d. $15.50
811.3. Consider a put option a non-dividend paying asset with two years to maturity. The put option's strike price is $100.00 and the asset's price is currently $94.00, so the option is currently in-the-money (ITM). Patria the Risk Analyst estimated the option's price with a two-step biniomial such that each step is one year, as illustrated below:
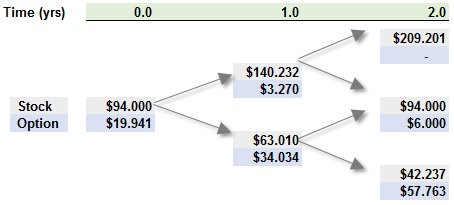
Patricia estimated the asset has a volatility of 40.0% per annum, and she assumed a risk-free rate of 3.0%. Her calculation for the risk-neutral probability of the asset price going up in a single step is 43.838%. According to her model, the option's value is $19.941. However, she realizes that she implicitly priced the option as if it were a European option, but in fact, this is an American-style option. In this way, price assigns no value to the option's early exercise feature. Which is nearest to the valuation error; i.e., what is the difference in the current price if model treats the option as an American-style option?
a. $1.61
b. $2.87
c. $2.96
d. Zero difference (the option is in-the-money)
Answers here:
Questions:
811.1 Consider a six-month at-the-money (ATM) European call option on a non-dividend-paying stock with a current price of $80.00. Peter the Risk Analyst has employed a two-step (i.e., three months per step) binomial model to price the option, as displayed below:

Peter's model matches the up and down movements to his estimate of the stock's prospective volatility, which he assumes is 34.0% per annum. The risk-free rate is 4.0%. Which of the following is nearest to the risk-neutral probability of the stock price going up in a single step?
a. 45.61%
b. 46.44%
c. 48.70%
d. 52.52%
811.2. Consider a European call option on a non-dividend-paying stock. The strike price is $80.00 while the stock price is currently $90.00. Barbara the Risk Analyst employs a two-step (i.e., three months per step) binomial model to price the option, as shown below:

Barbara estimates the volatility of the stock is 26.0%, and she assumes the riskfree rate is 3.0%. Which of the following is nearest to her estimate of the price of the option?
a. $12.97
b. $13.84
c. $14.35
d. $15.50
811.3. Consider a put option a non-dividend paying asset with two years to maturity. The put option's strike price is $100.00 and the asset's price is currently $94.00, so the option is currently in-the-money (ITM). Patria the Risk Analyst estimated the option's price with a two-step biniomial such that each step is one year, as illustrated below:

Patricia estimated the asset has a volatility of 40.0% per annum, and she assumed a risk-free rate of 3.0%. Her calculation for the risk-neutral probability of the asset price going up in a single step is 43.838%. According to her model, the option's value is $19.941. However, she realizes that she implicitly priced the option as if it were a European option, but in fact, this is an American-style option. In this way, price assigns no value to the option's early exercise feature. Which is nearest to the valuation error; i.e., what is the difference in the current price if model treats the option as an American-style option?
a. $1.61
b. $2.87
c. $2.96
d. Zero difference (the option is in-the-money)
Answers here:
