Learning objectives: Define and describe the key features of a futures contract, including the asset, the contract price and size, delivery, and limits. Describe the rationale for margin requirements and explain how they work. Describe the mechanics of the delivery process and contrast it with cash settlement. Compare and contrast forward and futures contracts
Questions:
708.1. The following six trades occur during a futures trading session among participants Albert, Barbara, Chris, Donald, Erin and Fred:
a. No change to open interest
b. Increase of 250 contracts
c. Increase of 425 contracts
d. Decrease of 50 contracts
708.2. Which of the following items is the LEAST LIKELY to be among the specifications of a futures contract?
a. Price and/or position limits
b. Grade and quality of the asset
c. Level of of required variation margin
d. Delivery location(s) and delivery months
708.3. The table below itemizes an investor's long position gold futures contracts. On the first day, the investor buys ten (10) contracts when the futures price is $1,200.00. Because the initial margin is $6,000 per contact, the investor must deposit a total of $60,000 in the margin account. The maintenance margin is $4,000 per contract. Over the subsequent eight days, the futures price fluctuates as shown.
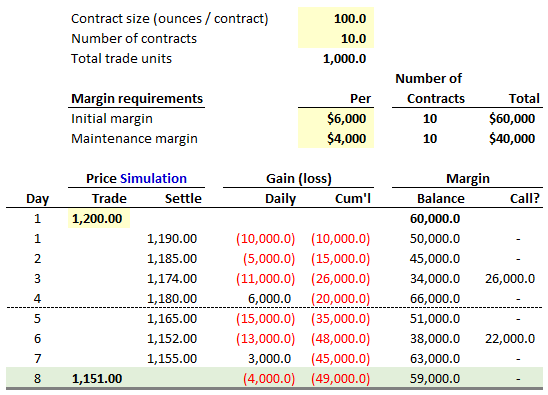
Which is following statements about this scenario is TRUE?
a. The investor has excess margin on two of the days
b. The margin calls are triggered only when the investor closes out contracts
c. The simulation is missing margin calls on days one (1), two (2) and five (5)
d. The investor's holding period return is a loss of about 1.67% which is equal to -1,000 ÷ 60,000
Answers here:
Questions:
708.1. The following six trades occur during a futures trading session among participants Albert, Barbara, Chris, Donald, Erin and Fred:
- Trader Albert (A) enters a new long position buying 300 futures contracts from Trader Barbara (B) who is the corresponding seller entering a new short position
- Trader Chris (C) enters a new long position buying 250 futures contracts from Trader Donald (D) who is the corresponding seller entering a new short position
- Trader Albert (A) offsets all 300 of his existing long contracts by selling to Trader Erin (E) who is the corresponding buyer entering a new long position
- Trader Chris (C) offsets 125 of her existing contracts by selling to Trader Fred (F) who is the corresponding buyer entering a new long position
- Trader Erin (E) offsets 150 of her existing long contracts by selling to Trader Barbara (B) who is the corresponding buyer who offsets 150 of her existing short contracts
- Trader Barbara (B) forgets to offset and is forced to deliver on her short position in her remaining 150 contracts; and she delivers to Trader Erin (E) according to her existing long contacts
a. No change to open interest
b. Increase of 250 contracts
c. Increase of 425 contracts
d. Decrease of 50 contracts
708.2. Which of the following items is the LEAST LIKELY to be among the specifications of a futures contract?
a. Price and/or position limits
b. Grade and quality of the asset
c. Level of of required variation margin
d. Delivery location(s) and delivery months
708.3. The table below itemizes an investor's long position gold futures contracts. On the first day, the investor buys ten (10) contracts when the futures price is $1,200.00. Because the initial margin is $6,000 per contact, the investor must deposit a total of $60,000 in the margin account. The maintenance margin is $4,000 per contract. Over the subsequent eight days, the futures price fluctuates as shown.

Which is following statements about this scenario is TRUE?
a. The investor has excess margin on two of the days
b. The margin calls are triggered only when the investor closes out contracts
c. The simulation is missing margin calls on days one (1), two (2) and five (5)
d. The investor's holding period return is a loss of about 1.67% which is equal to -1,000 ÷ 60,000
Answers here:
